Pantex Blog
Progress continues at the ASC

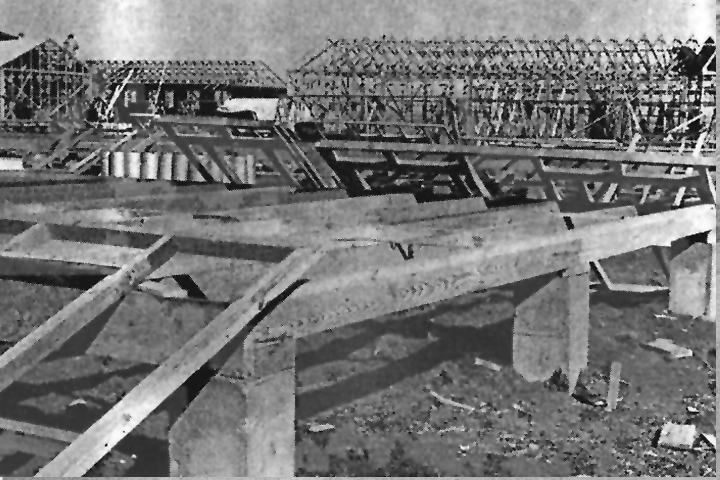
The skyline around Pantex continues to change as work at the Administrative Support Complex progresses. What was a field of milo this time last year is now an expansive building that grows closer and closer to completion with each passing day. Currently, the ASC is on schedule, and several areas of the building are nearing completion.
With the exterior nearly finished, the work indoors has begun to ramp up. For example, on the third floor of the west wing, drywall, painting, the break room, and bathrooms are complete and will serve as the mockup for the remaining break rooms and bathrooms for the rest of the building.
Major mechanical equipment, such as chillers, air handlers, plumbing lift station, and electrical transformers, have now been installed, and the domestic water line between the ASC and Pantex is now in operation. Not only is the skyline changing but traffic and roads are as well. The acceleration and de acceleration lanes on FM 2373 were completed recently and will provide relief for traffic entering and exiting the ASC area.
Upcoming milestones include the completion of the overhead power and the exterior envelope of the building, which is scheduled to take place this month. This month, crews will begin installing furniture, and the parking lot should be completed.
With the progress comes more people working at the ASC site. The number of workers has reached its peak.
Mentoring matters
Starting a new job can be anxiety producing. The situation can be nerve-racking unless you have a “coach” to support you.
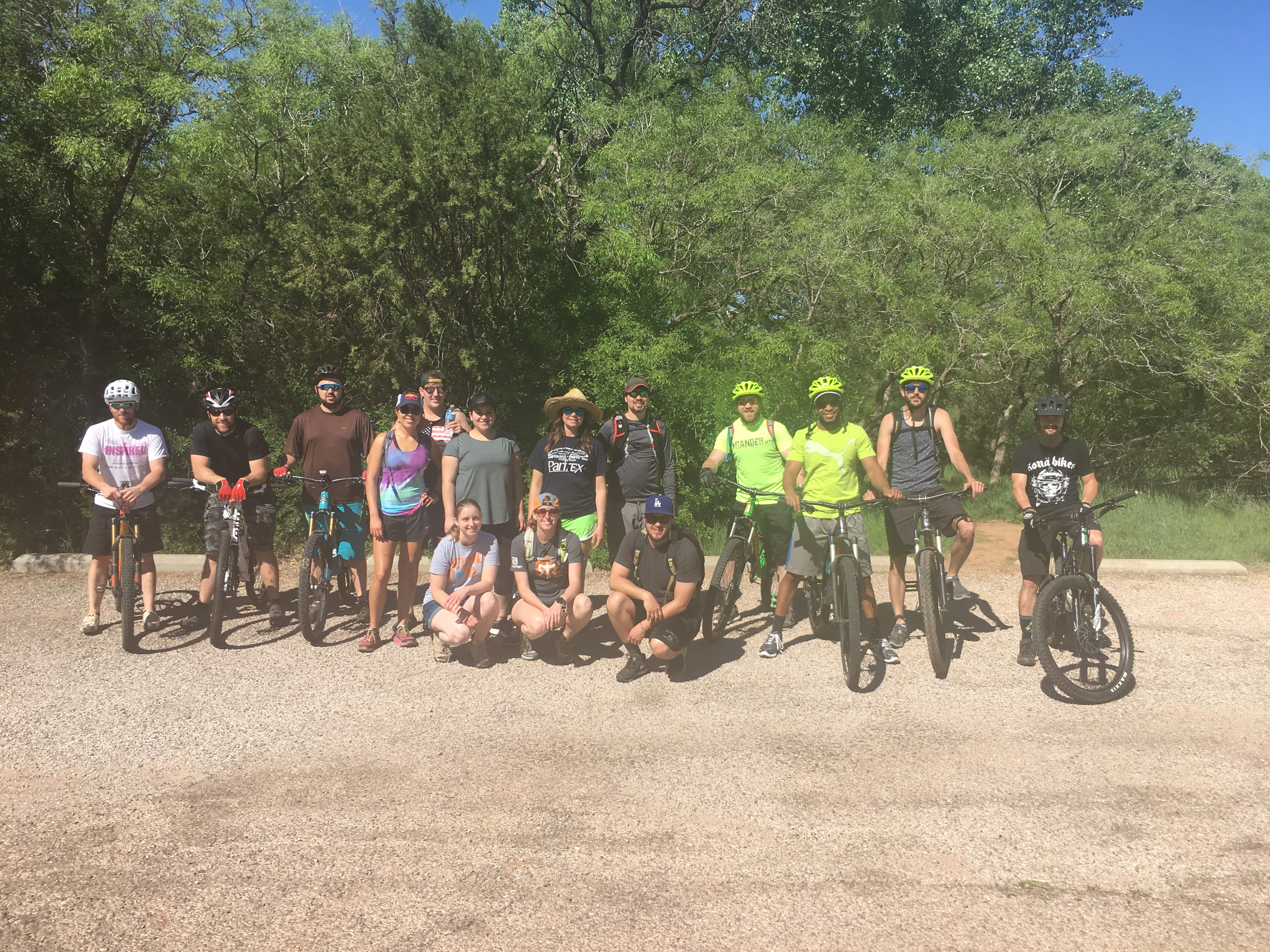

POLO group during their Second Annual Hike and Bike at Palo Duro Canyon State Park.
For Trent Spivey, that coach was Courtney Waddell from Pantex Facility Engineering. Spivey spent considerable time awaiting his clearance in a trailer located just outside the protected area. Fortunately, Waddell stopped by regularly to ask how she could help make his transition into the company as easy as possible.
“Without Courtney, I would have known nothing about Pantex nine months after being hired,” Spivey said. “Coming to a place with more than 3,000 people that you don’t know, it helps to have a friend.”
Spivey learned about Pantex while attending West Texas A&M and as a student had the opportunity to take a site tour and meet with different managers. Once on board, he joined the Pantex Outreach and Leadership Organization, a group of early career professionals in STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) fields, where Waddell volunteered to be his mentor.
“Having a mentor to introduce me to the people I’d be working with put me further ahead than those who came in blindly. That’s the number one success of the mentoring program,” Spivey said. “The mentorship really plugged me in and showed me what I can be within the company.”
Spivey now is on the POLO social subcommittee, and he looks forward to one day passing on what he knows to other new employees.
Chris Whitmer is one of the original organizers of POLO. Since its formation in 2014, POLO has grown to more than 100 members who participate in various networking, social, and community events. At a recent networking event, engineers toured the inside of a turbine at the Pantex wind farm, and at another, they heard an engineer talk about career paths, technical versus management, based on his own experience.
“POLO gives new hires, especially those coming from areas outside of Amarillo, the opportunity to meet other people, which gives them a reason to stay,” said Whitmer, who is from Las Cruces, New Mexico.
Barbara Vertefeuille from Safety Analysis Engineering, shares Whitmer’s viewpoint.
“If people have someone to go to—someone to ask questions and point them in the right direction—they are more likely to stay,” she said.
Vertefeuille has taught training for the last 20 years and has mentored those who are working toward their Documented Safety Analysis qualifications. She focuses on the specialized abilities they need for the work and helps them understand their role.
“People need someone to help them progress in their job and lives. I try to help them feel comfortable and confident in their own abilities,” she said.
Pantex SPO receives national honor
Pantex security police officer Billy Hall was recently recognized as one of the best in the U.S. Department of Energy Complex.
Hall is the latest recipient of the Colonel Sydnor Award, named after Colonel Elliot P. Sydnor, who had a large impact in the modernization of the Savannah River Site’s Protective Force in 1983. Sydnor would go on to help develop the Department of Energy’s Composite Adversary Team.

Billy Hall (center) receives the Colonel Sydnor Award from Ben Bitonel (left) and Kerry Wisniewski.
In honor of Colonel Sydnor, the Office of Enterprise Assessments presents the award annually to a CAT member who demonstrates the highest level of physical fitness and tactical proficiency and exhibits qualities associated with superior character and leadership.
“The Composite Adversary Team represents the most talented Security Police Officers across the DOE complex,” Protective Force Deputy Chief Daniel Holmes said. “It is very difficult to be selected to be a part of the CAT program.”
Hall has been a part of the Special Response Team at Pantex for 14 years and is now an SRT captain. He said that the position has given him many tools that have allowed him to be a more effective leader for his team.
“Being selected for this award by my peers — from all of the other DOE sites — as the Colonel Sydnor winner is the greatest accomplishment in my career thus far,” said Hall. “Finally reaching this goal has been very gratifying and required much hard work, patience, dedication and love for what I do.”
The DOE CAT Program’s level of excellence is recognized throughout the worldwide nuclear security community, and Pantex has risen to the occasion before. Hall is the third Pantexan to receive this honor in the last 20 years.
Historical Pantex: A village is born
In 1943, housing was at a premium in the Amarillo area. With the war effort and production at Pantex already in full swing and a growing workforce, the need for new homes was obvious.
Construction of pre-fab housing units at the Pantex Village.
The National Housing Administration approved 175 new homes to be built in Amarillo for Pantex employees with 3 or more family members, but even that number was not sufficient. So, an additional 360 units were approved including 142 two-room apartments, 128 one-bedroom apartments, 60 two-bedroom units and 30 with three bedrooms.
It was all part of what was then called “Pantex City,” which was located just north of U.S. Highway 60 and Farm-to-Market Road 683. Initially, along with apartment buildings and homes, plans for the city included a shopping center with a grocery store, meat market, fire station, drug store, barber shop, beauty parlor, shoe repair and a tailor shop. There was also talk of a possible grade school with plans to bus students back to town for high school.
Construction was slated for completion in April 1943, thanks to pre-fabricated, mass-production methods. The apartment buildings went up like Tinker Toys with each dwelling having between four to eight apartments. An additional 400 pre-fab homes were soon added, bringing the population of the Pantex Village up to a few thousand. The village grew to 69 residence buildings, a community center and a store to support the approximately 5,325 employees at Pantex working 3 shifts at the height of World War II.
Noted cowboy poet and author Buck Ramsey lived at the village, according to a 1977 article called “Letter from the Panhandle,” which was printed in the Texas Observer magazine. In it, he reminisced about his time at Pantex.
“On the western edge, the government constructed a village; symmetrical rows of buildings so uniform there was a nightly problem of entering the wrong apartment by mistake. The war industry, with its promise of regular paychecks and dwellings with gas heaters and indoor plumbing, lured many families from the hardscrabble countryside. Mine was among them.
“I sometimes slipped through the fences to wander about the forbidden pastures, to lie on my back in the ungrazed grass… and listen to trains rumble away with bombs for Europe and Asia. The war ended with me seven years old. For a couple more years we lived in the village, while the munitions plant deteriorated from the peace. I grew bolder with age and would climb up to survey the area from watchtowers. I walked the barracks porches, and then broke into deserted buildings to steel my nerves against the ghosts inside, preparing myself for some future war.”
Ramsey noted in his writings about the barren countryside and how set apart the village seemed to be from the rest of the area.
In fact, the village was very isolated, functioning as a self-sufficient community. It was 10 miles from the town of Panhandle and accessed only through a perimeter gate that was locked each evening. There were recreational facilities, especially for the younger set, including basketball and tennis courts along with a teen club where dances took place.
To some outsiders, the village was known as the low-income “Cardboard Village” due to the pre-fab materials and walls so thin you could hear neighbors talking.
As a village, there was also a small newspaper called the Pantex Breeze. There were no real village officials because the place was run like a housing project. There was a manager, but no one was ever elected as an official to preside over the village.
After the war, things started to change. In 1949, the plant and village were acquired by Texas Technological College (now Texas Tech University) in Lubbock, and, by the end of that year, the village was turned over to Carson County.
The village was still going strong in the early 1950s. According to housing advertisements in the Pantexan magazine, the rent for a one- to three-bedroom apartment ranged from $33 to $42 per month, with all utilities paid.
In 1968, Pantex Village closed due to the large number of vacancies caused by improved economic opportunities elsewhere and the closing of the Amarillo Air Base in 1967.
Eventually, ads were placed throughout the Panhandle that the buildings were all to be sold at auction. Some of the smaller buildings are reportedly still being used in the town of Panhandle as a storage shed and another as a re-bricked building. Today, all that’s left as a reminder of the early days of the facility and the role it played at the Pantex Plant are a few concrete slabs dotted around the area where the village once stood.
However, the most surprising remnant of the auction is right down Interstate 40 as you enter Amarillo. On the east side of town, you will find one of the most advertised and well visited tourist destinations, the Big Texan Steak Restaurant, famous for its “free 72-ounce steak, if eaten within an hour.”
Bob Lee purchased and dismantled five barracks picked up at the auction and used the lumber to build his restaurant in 1960. Reportedly, most of that wood was lost in a fire in 1976, but the restaurant was rebuilt with the help of 100 of his employees pitching in.
Just like a time more than 30 years earlier… it took a village.
Smart Play
With nearly three-fourths of the workforce at the Pantex Plant only five years away from retirement age, Consolidated Nuclear Security (CNS) has put a heavy focus cultivating our future workforce.
Data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) states that employment in occupations related to STEM – science, technology, engineering, and mathematics – is projected to grow to more than 9 million between 2012 to 2022. Something that we know first-hand.
In 2015, CNS donated $10,000 to Bushland Independent School District (BISD) to help them kick-start an initiative to create a hands-on, high-tech STEM educational program.
The district knew there was a need to provide more STEM-related education. They decided that the best direction to implement this initiative was to form elementary, middle, and high school teams that would participate in FIRST® (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology), international robotics competitions that drive students to research and explore real-world scientific and engineering challenges.
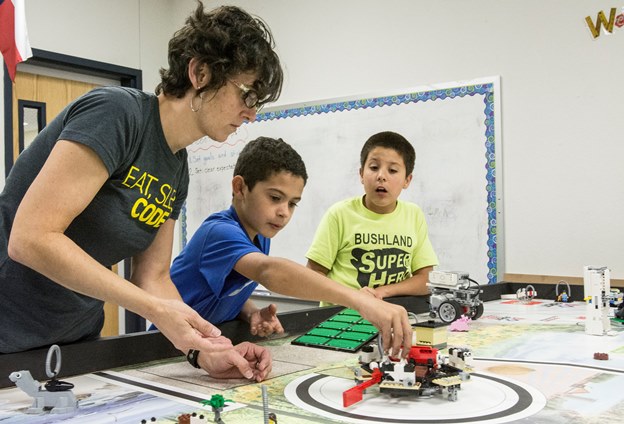

The teachers responsible for building this multi-level robotics program agreed upon a plan that no one saw coming. The popular choice would have been to use the funds to immediately support the high school STEM program, but the teachers chose to take a different approach. One that would build a solid foundation for STEM education for years to come.
“Just like in sports. You don’t wait until high school to start building athletes,” said BISD teacher and robotics sponsor, Jessica Patterson. “The same is true for education. You don’t wait until college to build engineers.”
Jessica Patterson, who runs Bushland Elementary’s Einstein Lab, along with Melissa Cochran, who handles the computer lab, and Christina Butler, who teaches special education, have other daily responsibilities but were willing to devote nights and weekends to cultivate a program that would enhance students’ learning to the next level.
After hosting a “Get to Know Robotics Family Night,” students organized teams to create their own robot and research presentation. By May 2015, BISD had 11 FIRST LEGO® League Jr. (JrFLL) teams, seven FIRST LEGO League (FLL) teams, and one FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC) team. The question now was: How can we serve more than 100 students without sending every one of them to Dallas to compete in a tournament?
Thus began the TexPan Robotics tournament. BISD staff, in conjunction with Amarillo College Engineering Society and Amarillo Area Center for Advanced Learning (AACAL), created a robotics tournament to serve all local teams.
“We saw the need for all students in the Texas Panhandle to have a local tournament to compete and celebrate learning,” said Patterson.
Currently, TexPan robotics is working with FIRST to become an official region for students in the panhandle. The 2015 tournament champions were The Purple Perspicacious Pandas, a group of six middle school girls who defeated their competitors to receive an ACE (Advancing to Championship) certificate allowing them to travel to Dallas to compete in the North Texas FLL Regional Championship in February 2016.
After tournament season ended, the Bushland Robotics teachers (otherwise known as the LEGO Ladies) devised a plan to rollout a “WE Do STEM” and EV3 robotics academy. The “WeDo STEM” academy serves students in kindergarten through second grade, and EV3 academy serves third through eighth grade. This six-week robotics academy was held outside of normal school hours and began teaching the basic skills of building and programing a robot. Later, academies addressed programming sensors and precision programming.
“We chose to keep to six-week learning programs because the short learning process engages kids to learn rather than just show up for a club meeting,” explained Patterson.
The academy was full within a matter of minutes of registration opening, showing the teachers that there was obviously an interest by the students and it was backed by their parents. The spring academies sparked such an interest in the students and their parents, that BISD now has seen a growth in teams to 11 JrFLL, 10 FLL, and two FTC teams. An outside interest has added two additional FLL teams from the local homeschool community and from the Boy Scout council.
“Without the donation from Pantex, this program would not have been possible,” said Patterson. “The students’ learning is so rapid that we are moving faster than we could have imagined and these resources provided by Pantex are an essential part to our success.”
Pantex provided BISD with another $10,000 contribution for the 2016–2017 school year in an effort for them to expand their program to the FTC for 7–12 grade students and eventually a FIRST Robotics Challenge team for 10–12 grade students.
